1. Usability
- Learnability: Make it easy for users to learn how to use your product, providing clear instructions, tooltips, and onboarding experiences.
- Efficiency: Streamline user workflows, minimizing the number of steps and interactions required to complete tasks.
- Memorability: Design your product so that users can easily remember how to use it, even after extended periods of disuse.
- Error prevention and recovery: Help users avoid errors by providing clear guidance and validation, and offer easy ways to recover when errors do occur.
Example of Good Usability: Slack
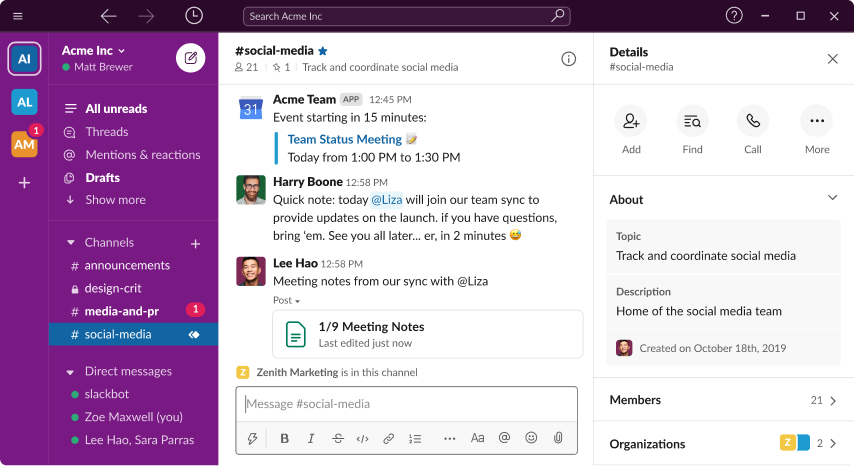
2. Consistency
- Visual consistency: Maintain a consistent visual design, including colors, typography, and UI elements, across all areas of your product.
- Functional consistency: Ensure that similar features and interactions behave consistently, so users don't have to relearn how to perform tasks.
- External consistency: Align your product with established conventions and standards within your industry or platform, leveraging familiar design patterns and interactions.
Example of UI Consistency: Google Suite
3. Feedback
- Visual feedback: Use subtle animations or color changes to indicate the state of UI elements (e.g., buttons changing color when clicked).
- Auditory feedback: Employ sounds to communicate success, errors, or other important events (e.g., a chime when a message is sent).
- Tactile feedback: Utilize haptic feedback (vibrations) to provide a physical response to user actions (e.g., a vibration when selecting an option on a touchscreen).
Example of User Feedback: Apple iOS

4. Flexibility and Efficiency
- Customization: Allow users to personalize your product to better suit their preferences and needs, such as changing color schemes, font sizes, or interface layouts.
- Shortcuts and accelerators: Provide shortcuts, hotkeys, or other efficiency-enhancing tools for expert users, enabling them to complete tasks more quickly.
- Adaptability: Design your product to work seamlessly across different devices, platforms, and input methods, ensuring a consistent experience for all users.
Example of Flexible UI: Trello
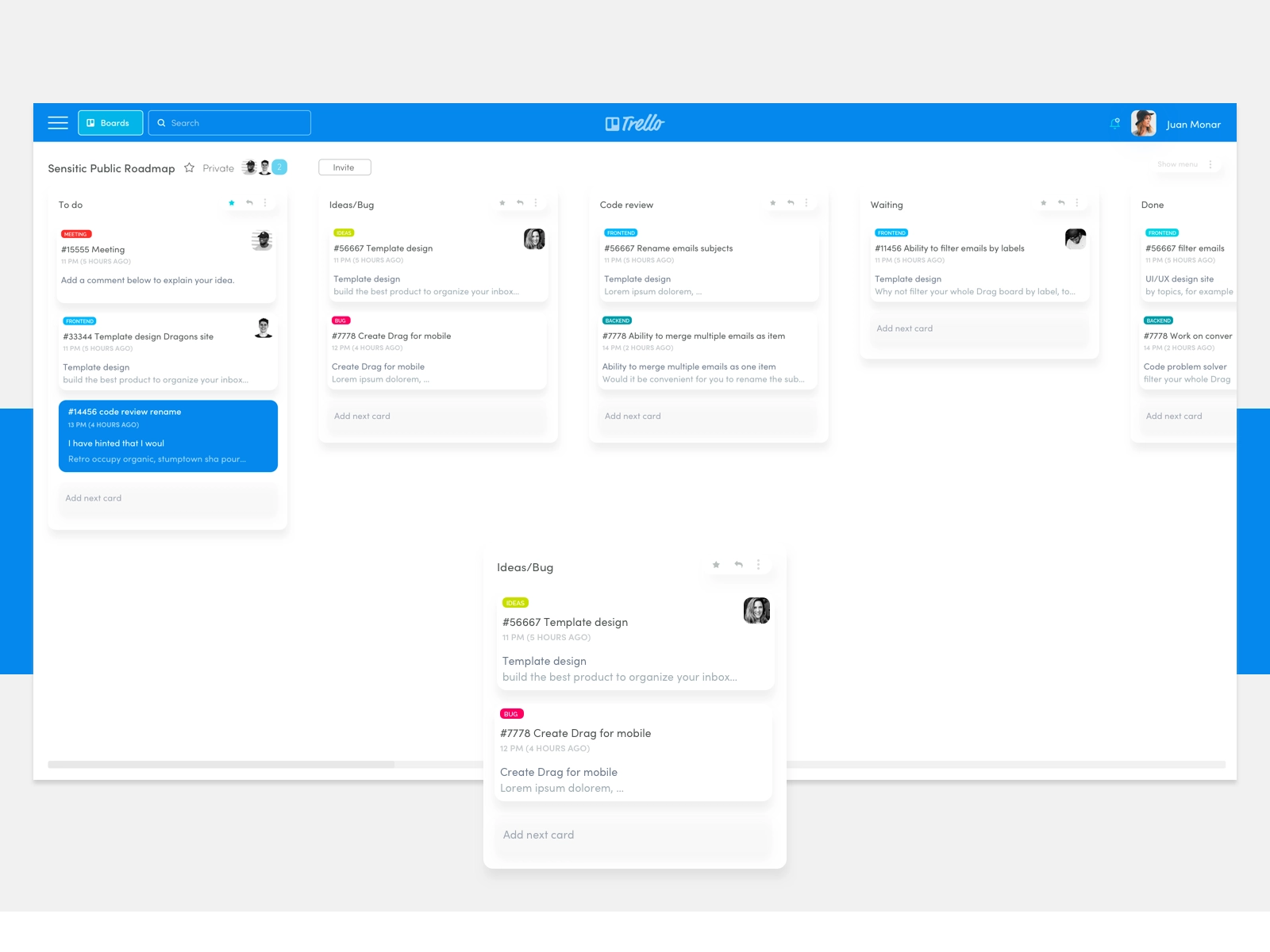
5. Emotional Design
- Aesthetics: Craft an aesthetically pleasing visual design that creates a positive emotional response and conveys a sense of quality and professionalism.
- Delight: Incorporate delightful details and interactions, such as engaging animations, humorous copy, or personalized content, to surprise and delight users.
- Empathy: Understand and address the emotional needs of your users, designing your product to support their goals, alleviate their pain points, and foster positive emotions.
Example of Emotion-Infused Design: Headspace
6. User-Centered Design Process
- User research: Conduct interviews, surveys, and observations to gather insights into your users' needs, goals, and pain points.
- Prototyping and iteration: Create low- and high-fidelity prototypes of your product and iterate on them based on user feedback and testing.
- Usability testing: Test your product with real users to identify potential issues, validate design decisions, and gather insights for future improvements.
Example: Airbnb

Related Courses
Master UX Design for AI
Learn to design AI products that are intuitive and valuable. Build your AI project portfolio, get certified as an expert in UX for AI
User Interview Skills for Designers & PMs
Hands-on practice & expert guidance to 10x your interview skills. Get insights that power smart, data-driven product & design decisions.
Mastering AI Product Strategy: From Ideas to MVP
Learn the AI skills you need to evaluate opportunities, design experiences, and build AI-powered products—without coding
Design Manager Foundations
Aspiring or new-ish Manager? Step into UX Mgmt with the vetted knowledge, skills and frameworks from an expert Design Leader.
UX & Design Leadership Demystified
Learn the strategies, practices, and mindsets of successful design leaders.
You might also like

Gamify Your Product: Techniques for Boosting User Engagement

6 Effective Product Prioritization Frameworks & Techniques

